Operating from its headquarters in Tallinn, Estonia, Reverse Resources (RR) stands at the intersection of technology, supply chain management, and environmental sustainability. The company’s core mission is to solve one of the fashion industry’s most pressing and complex challenges: textile waste. By focusing on digitalization and transparency, RR is enabling a systemic shift that reduces the industry’s dependency on virgin materials and scales up textile-to-textile (T2T) recycling globally.
The company’s driving philosophy is rooted in the conviction that “There is no such thing as waste in the textile industry — only a valuable resource that presents unexplored business opportunities,” a sentiment often shared by founder and CEO, Ann Runnel. Reverse Resources believes the pathway to climate action and the reduction of environmental impact lies in efficient resource reuse, necessitating the establishment of profitable and traceable circular business models on a massive scale. Their practical “elevator pitch” is simple: RR is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) impact platform digitising, connecting, scaling, and tracing textile waste to enable global textile-to-textile recycling and compliance with new circularity legislation.

A Journey from Research to Global Platform
Reverse Resources’ story began in 2014, initially focusing on research to map and understand the opaque world of textile waste flows. This early phase was critical, treating the problem not just as an environmental hazard but as an economic supply chain breakdown. Waste in the fashion industry, often treated as a “dirty secret” by stakeholders, lacked the data necessary for proper recovery and reuse.
A pivotal moment occurred in 2015 when the company was recognised as a winner of the H&M Foundation Global Change Award. This accolade not only provided crucial early funding but, more importantly, opened doors to the global fashion supply chain, allowing the team to move beyond concept testing into real-world application. For the first five years, the Estonian startup functioned largely as a mapping organisation, uncovering the critical missing links, e.g. lack of quality data, fragmented supply chains, and insufficient segregation at the source, that hampered high-end recycling.
This intensive research eventually led to the development and launch of the RR digital platform, restructuring the company’s focus from a research initiative into a digital supply chain infrastructure provider. Today, Reverse Resources is no longer just mapping waste; it is actively directing it, building reliable, data-driven feed stock supply chains necessary for the T2T recycling sector to scale.

Innovation Through Digital Transparency
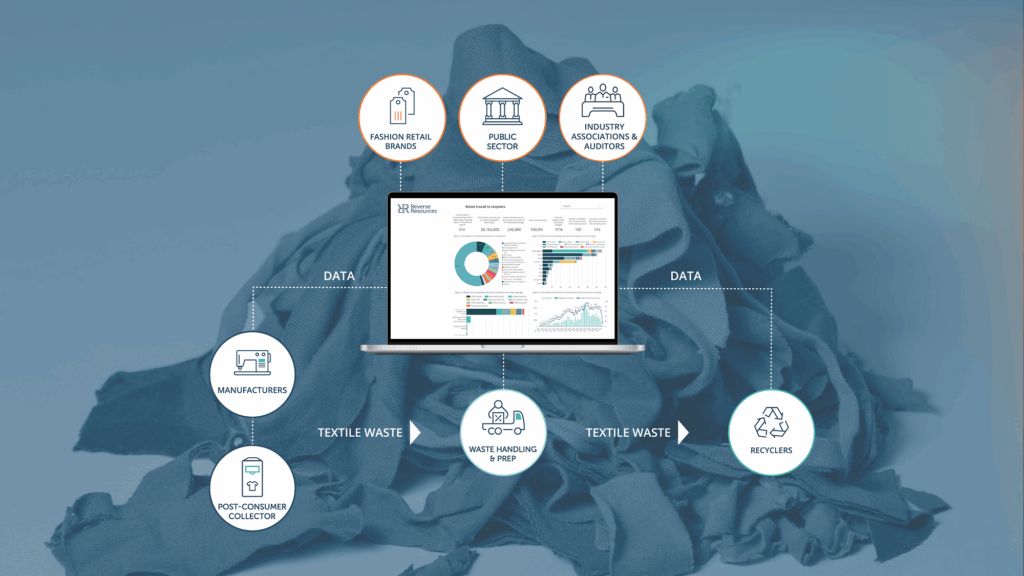
For Reverse Resources, innovation is not defined by inventing a new recycling technology, but by digitising and standardising the global flow of materials to make existing and emerging technologies commercially viable. The company’s innovative edge lies in its commitment to full traceability and transparency, embedded directly into the daily operations of the supply chain.
The Reverse Resources SaaS platform connects manufacturers (waste generators), waste handlers, recyclers, and global brands in a single digital environment. Manufacturers can report and segregate waste directly at the cutting table, elevating the quality and value of industrial offcuts. Recyclers, in turn, gain real-time visibility into available, pre-verified, and traceable feedstock that meets their technical specifications.
The platform ensures that data is captured and verified at the source, solving the historic problem of accessing high-quality, known-composition waste. This digital infrastructure shortens supply chains, reduces sorting costs, and provides brands with the ability to govern their waste and demonstrate third-party verification on their closed-loop recycling efforts. As CEO Ann Runnel notes, the platform’s job is to create “a new business logic for the fashion industry,” proving that resource efficiency and profit can, and must, align.
The Tipping Point of Global Demand
The acceleration of Reverse Resources’ growth was fundamentally enabled by two coinciding market forces: the explosion of new T2T recycling technologies and the increasing regulatory and consumer pressure on brands to commit to circularity.
When the company began, T2T recycling was nascent. Today, the industrial capacity for textile recycling is rapidly expanding, but growth is hampered by a lack of reliable, high-quality material input. This feedstock scarcity became the company’s tipping point, positioning the RR platform as the essential infrastructure to unlock that latent recycling capacity.
RR has now digitally mapped and tracked over 120,000 tonnes of textile waste across 38 countries, with approximately 50% of this volume successfully traced to T2T recycling. Its network includes 1,500 profiled manufacturing facilities, 264 verified recyclers, and six offices across Europe and Asia. These numbers represent a significant leap beyond the early pilot stage, demonstrating the platform’s ability to operate at global scale.

Contributing to the Ecosystem and Future Vision
Reverse Resources is a key nexus point in the global textile innovation ecosystem, collaborating through multi-stakeholder initiatives such as the Circular Fashion Partnership (led by Global Fashion Agenda) and projects with Fashion For Good, UNIDO, GIZ, as well as newer EU-supported programs including the T2T Recycled Fiber 2030 initiative, PESCO-UP, SAGE, and SMEP. By embedding teams close to major manufacturing hubs while keeping its innovation backbone in Estonia, RR ensures that its solutions address waste at the source and scale efficiently.
Looking ahead, the team is most excited about expanding its scope beyond post-industrial cutting scraps into the massive challenge of post-consumer textile waste. RR is developing functionality to integrate this new waste stream and act as a trusted data backbone for the EU Digital Product Passport, enabling seamless sharing of verified waste and recycled content information across the supply chain. Its vision is to help the fashion industry secure reliable, high-quality recycled fiber feedstock and meet rapidly approaching circularity legislation while reducing dependence on virgin resources.
In its final message, Reverse Resources asserts that achieving full circularity in the textile industry is not a distant dream but an achievable reality when the right digital tools and collaborations exist. By demonstrating a viable, profitable business case for resource reuse, the company is proving that the economic viability of circularity is inextricably linked to the quality and transparency of data. RR is not waiting for policy to dictate action; it is proactively building the digital infrastructure the industry will rely on for its circular future.















